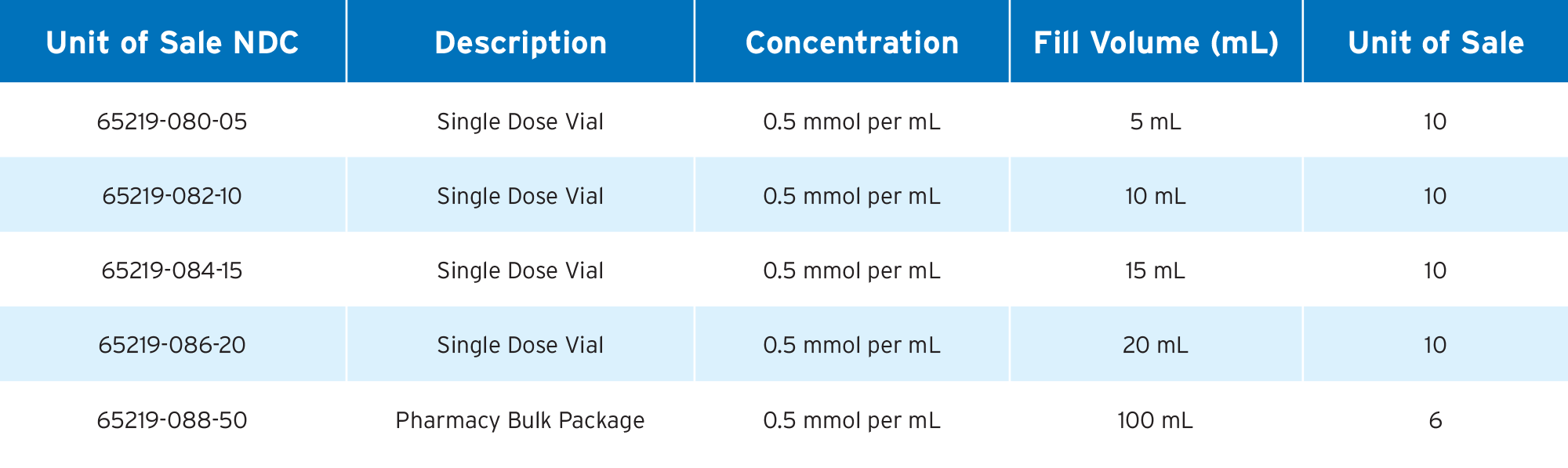
Products
Important Safety Information | Medication Guide | Full Prescribing Information: Single Dose Vials / Pharmacy Bulk Package
Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP
Macrocyclic & Ionic Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent3,4
Fresenius Kabi’s FDA-approved generic Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP provides an option that is bioequivalent and fully substitutable to Dotarem®.*
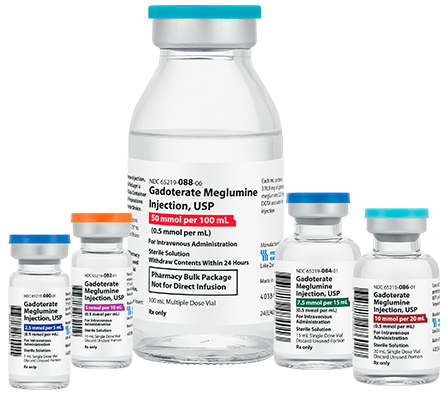
Fresenius Kabi’s Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP is fully substitutable to Dotarem®.*
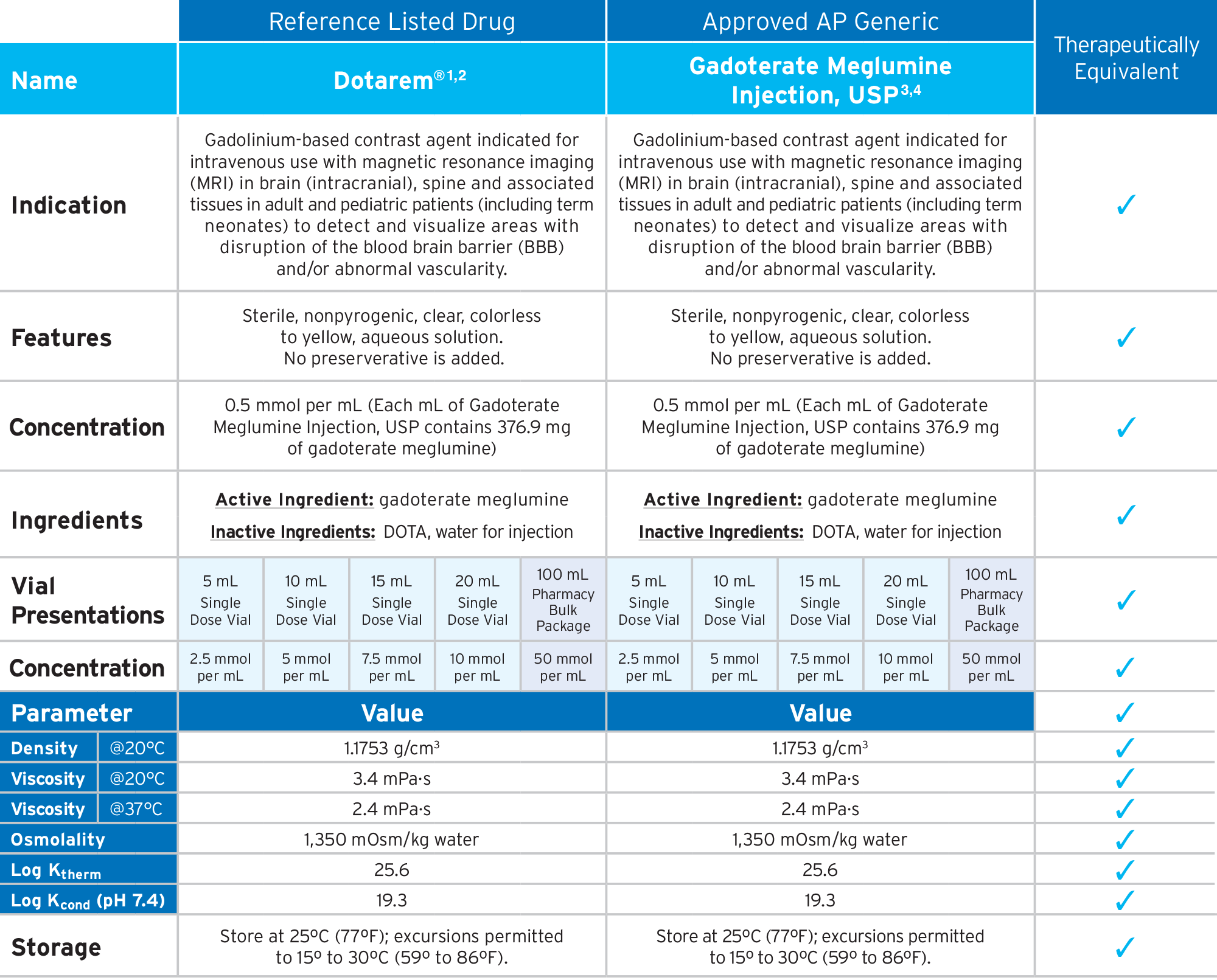
Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP
• FDA-approved, AP Rated
• Macrocyclic3,4
• Ionic3,4
• Preservative Free3,4
• The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex
• Bioequivalent and fully substitutable to Dotarem®*
1. Dotarem Single Dose Vial Package Insert, March 2025
2. Dotarem Pharmacy Bulk Package Insert, March 2025
3. Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP Single Dose Vial Package Insert, May 2025
4. Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP Pharmacy Bulk Package Insert, May 2025
*Dotarem® is a registered trademark of Guerbet.
Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. Gadoterate Meglumine Injection is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
CONTRADICTIONS
Gadoterate Meglumine Injection is contraindicated in patients with history of clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to Gadoterate Meglumine Injection.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection have not been established with intrathecal use. Gadoterate Meglumine Injection is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory or cutaneous manifestations, ranging from mild to severe, including death, have uncommonly occurred. Monitor patients closely for need of emergency cardiorespiratory support. Before Gadoterate Meglumine Injection administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to Gadoterate Meglumine Injection.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in brain, bone, and other organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection. Extravasation into tissues during Gadoterate Meglumine Injection administration may result in tissue irritation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent (≥ 0.2%) adverse reactions in clinical trials were nausea, headache, injection site pain, injection site coldness, and rash.
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of gadoterate meglumine or other GBCAs:
- Cardiac Disorders (bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia).
- Immune System Disorders (hypersensitivity / anaphylactoid reactions including cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, cyanosis, pharyngeal edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, angioedema, conjunctivitis, ocular hyperemia, eyelid edema, lacrimation increased, hyperhidrosis, urticaria).
- Nervous System Disorders (coma, convulsion, syncope, presyncope, parosmia, tremor).
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders (muscle contracture, muscle weakness).
- Gastrointestinal Disorders (diarrhea, salivary hypersecretion, acute pancreatitis with onset within 48 hours after GBCA administration).
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions (malaise, fever), Adverse reactions with variable onset and duration (fatigue, asthenia, pain syndromes, and heterogeneous clusters of symptoms in the neurological, cutaneous, and musculoskeletal systems).
- Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders (Acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema).
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders (NSF, in patients whose reports were confounded by the receipt of other GBCAs or in situations where receipt of other GBCAs could not be ruled out. No unconfounded cases of NSF have been reported with gadoterate meglumine. Gadolinium-associated plaques).
- Vascular Disorders (superficial phlebitis).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176, option 5, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence of gadoterate in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk.
Pediatric Use: The safety of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection has not been established in preterm neonates. No dosage adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use: Use of Gadoterate Meglumine Injection in elderly patients should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of impaired renal function and concomitant disease or other drug therapy. No age-related dosage adjustment is necessary.
Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gadoterate Meglumine Injection is a prescription gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain (intracranial), spine and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP safely and effectively. Please see full prescribing information, including BOXED WARNING, for Gadoterate Meglumine Injection, USP Single-Dose Vials and Pharmacy Bulk Package. Full prescribing information is also available at www.fresenius-kabi.com/us.